4. Create Custom Scores¶
Scores are what HAWK uses to increase or decrease the wight/score of each event. The following information will help you create new custom Scores or edit existing Scores.
The Scores get processed on the HAWK engines (hawk-analyticsd service). HAWK eyeCon 5.0 comes with 65 Default scores. It is recommended that the customer create new scores that fit their network polices.
4.1. Module Keys¶
When adding rules to scores the following Module Key columns or functions can be used.
4.1.1. Columns¶
- bayesian_weight (float):¶
Bayesian score showing the probability of the event being good or bad. SOC Analyst can tune the Bayesian algorithm by marking learning events as bad or good.
- weight (float):¶
Commutative weight assigned to a event based off Analytic Scores.
- date_added (string):¶
Date event was added to the HAWK system.
- hid (string):¶
HAWK ID, HAWK assigned ID associated to the Alert Name. Click HERE to see a full list of available HAWK ID’s.
- alert_name (string):¶
Alert name assigned to the event.
- priority (integer):¶
Priority, Values 1 - 5. One being the highest priority and five being the lowest priority.
- app (string):¶
Application, Application event is from. Using map-replace on HAWK engines you can map application id’s to application names.
- action (string):¶
Action performed. A few examples: “quarantined”, “ignored”, “removed”
- alerts_type_name (string):¶
Alert Category assigned to the event. Click HERE to see a full list of Alert Categories.
- blocked (boolean):¶
True or False if the event was blocked.
- vendor_id (string):¶
Vendor assigned id. A few Examples: Windows event ids, Snort ids, Cisco ids (3-710003).
- resource_name (string):¶
Hostname of the resource sending the event.
- resource_addr (string):¶
IPv4 address of the resource.
- resource_asset_criticality (integer):¶
Resource asset criticality assigned to the resource.
- compliance_asset (boolean):¶
True or False if resource is a compliance asset.
- group_name (string):¶
Group Name assigned to resource.
- icmp_type (integer):¶
ICMP Type code. ICMP Types and Codes explained here
- icmp_code (integer):¶
ICMP Code. ICMP Types and Codes explained here
- icmp_csum (integer):¶
ICMP Checksum of event
- icmp_id (integer):¶
ICMP Identifier
- icmp_seq (integer):¶
ICMP Sequence
- ip_src (string):¶
IPv4 address of the sender of the packet
- ip_src_host (string):¶
Source hostname of the sender of the packet
- ip_src_geoip_name (string):¶
Source Address GeoIP Name
- ip_src_geoip_cc2 (string):¶
Source Address GeoIP Country Code
- ip_src_geoip_reg (string):¶
Source Address GeoIP Region
- ip_src_geoip_city (string):¶
Source Address GeoIP City
- ip_src_geoip_latitude (float):¶
Source Address GeoIP Latitude
- ip_src_geoip_longitude (float):¶
Source Address GeoIP Longitude
- ip_dst (string):¶
IPv4 address of the receiver of the packet
- ip_dst_host (string):¶
Destination hostname of the receiver of the packet
- ip_dst_geoip_name (string):¶
Destination Address GeoIP Name
- ip_dst_geoip_cc2 (string):¶
Destination Address GeoIP Country Code
- ip_dst_geoip_reg (string):¶
Destination Address GeoIP Region
- ip_dst_geoip_city (string):¶
Destination Address GeoIP City
- ip_dst_geoip_latitude (float):¶
Destination Address GeoIP Latitude
- ip_dst_geoip_longitude (float):¶
Destination Address GeoIP Longitude
- ip_sport (integer):¶
Identifies the sending port
- ip_dport (integer):¶
Identifies the receiving port
- ip_ver (integer):¶
IP Version: 4 = IPv4, and 6 = IPv6
- ip_hlen (integer):¶
IP Header Length
- ip_tos (integer):¶
IP Type of Service or Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP). IP header for packet classification purposes.
- ip_id (integer):¶
IP Identification. Primarily used for uniquely identifying the group of fragments of a single IP datagram.
- ip_flags (integer):¶
IP Flags used to control or identify fragments.
- ip_off (integer):¶
IP fragment offset field.
- ip_ttl (integer):¶
IP Time to Live.
- ip_proto (integer):¶
Defines the IP Protocol used in the data portion of the IP datagram. List of IP protocols here
- ip_csum (integer):¶
IP Checksum
- hash (string):¶
Stores the md5 hash of the raw payload.
- payload (string):¶
Raw event payload.
- packet (string):¶
Raw event packet if provided.
- tcp_seq (integer):¶
TCP Sequence number
- tcp_ack (integer):¶
TCP Acknowledgement
- tcp_off (integer):¶
Specifies the size of the TCP header
- tcp_res (integer):¶
TCP Reserved for future use and should not be used.
- tcp_flags (integer):¶
TCP Flags. Example ACK, RST, SYN, FIN. List of flags can be found here
- tcp_win (integer):¶
TCP Window size of the receiving window size in bytes.
- tcp_csum (integer):¶
TCP Checksum
- tcp_urp (integer):¶
TCP Urgent Pointer
- udp_len (integer):¶
Specifies the length in bytes of the UDP header and UDP data
- udp_csum (integer):¶
UDP Checksum
- class_type (string):¶
Host classification type. You can find a list of host classifications here
- class_name (string):¶
Host classification name. You can find a list of host classifications here
- os_type_name (string):¶
Operating System/Specific Vendor Name. You can find the full list here
- correlation_username (string):¶
Username
- target_username (string):¶
Target Username
- audit_login (boolean):¶
Audit Login
- audit_logoff (boolean):¶
Audit Logoff
- audit_policy_change (boolean):¶
Audit Policy Change
- audit_log_change (boolean):¶
Audit Log Change
- audit_object_access (boolean):¶
Audit Object Access
- audit_user_action (boolean):¶
Audit User Action
- audit_system_event (boolean):¶
Audit System Event
- audit_session_status (boolean):¶
Audit Session Status
- audit_account_validation (boolean):¶
Audit Account Validation
- audit_user_change (boolean):¶
Audit User Change
- audit_group_change (boolean):¶
Audit Group Change
- net_if_id (string):¶
Network Interface ID.
- net_if_collisions (string):¶
Network Interface Collisions
- net_if_packets (integer):¶
Network Interface Packets
- net_if_bytes (integer):¶
Network Interface Bytes
- net_if_in_packets (integer):¶
Network Interface Incoming Packets
- net_if_in_bytes (integer):¶
Network Interface Incoming Bytes
- net_if_in_dropped (integer):¶
Network Interface Incoming Dropped Packets
- net_if_in_errors (integer):¶
Network Interface Incoming Errors
- net_if_out_packets (integer):¶
Network Interface Outgoing Packets
- net_if_out_bytes (integer):¶
Network Interface Outgoing Bytes
- net_if_out_dropped (integer):¶
Network Interface Outgoing Dropped Packets
- net_if_out_errors (integer):¶
Network Interface Outgoing Errors
- net_if_name (string):¶
Network Interface Name
- health_service_ping (boolean):¶
Health Service Status Check
- sys_cpu_id (string):¶
CPU ID
- sys_cpu_load_total (integer):¶
CPU Total Load
- sys_cpu_load_user (integer):¶
CPU User Load
- sys_cpu_load_sys (integer):¶
CPU System Load
- sys_cpu_load_wait (integer):¶
CPU Wait Load
- sys_cpu_load_idle (integer):¶
CPU Idle Load
- sys_uptime (string):¶
System Uptime
- sys_version (string):¶
System Version
- sys_uname (string):¶
System Unique Name
- sys_mem_size_total (integer):¶
System Memory Total Size
- sys_mem_size_free (integer):¶
System Memory Free Size
- vm_mem_size_total (integer):¶
Virtual Memory Total Size
- vm_mem_size_free (integer):¶
Virtual Memory Free Size
- vm_mem_size_cached (integer):¶
Virtual Memory Cached Size
- vm_mem_size_buffers (integer):¶
Virtual Memory Buffers Size
- vfs_dev_id (string):¶
Filesystem Device ID
- vfs_dev_read_sectors (integer):¶
Filesystem Device Read Sectors
- vfs_dev_read_ops (integer):¶
Filesystem Device Read Operations
- vfs_dev_write_sectors (integer):¶
Filesystem Device Write Sectors
- vfs_fs_id (string):¶
Filesystem ID
- vfs_fs_size_total (integer):¶
Filesystem Total Size
- vfs_fs_size_free (integer):¶
Filesystem Free Size
4.1.2. Functions¶
- Stream Counter (atomic_counter):¶
Select the column or columns to count. Each column you select a distinct index will be created. For every unique value that matches they will be counted. If the count reaches configured threshold for the given time frame it will result in True.
- Distinct Stream Counter (atomic_distinct_counter):¶
This function allows you to select a column(s). Distinct column is unique column comparison to threshold within time limit.
- RBLDNS Blacklist Lookup (rbldns):¶
Set Host to either public or private RBLDNS service. Depending if its a blacklist or whitelist set the correct comparison. Select the Column you would like to compare to.
- Timestamp - Day of Week (time_dayofweek):¶
To apply a score to only certain days you can use this time stamp rule.
- Timestamp - Hour and Minute (time_hourminute):¶
to apply a score to only certain time frame in a day you can use this time stamp rule.
- Vulnerability Threshold Analysis (vuln_threshold):¶
This function allows you to select a column. Trigger if Severity comparison matches and threshold comparison matches.
- Inter-Column Comparison (column_comparison):¶
Compare two columns. Typically used to check if IP source and IP destination are not the same.
- Lookup List (case insensitive) (list_lookup):¶
Compare a column to specified list. One example is to compare correlation/target username to known bad actor usernames.
- Host Lookup List (host_lookup):¶
Compare a column to specified list.
- Host Lookup List (Live Resource) (host_lookup_resource):¶
Compare a column to a live Threat Intelligence list. To add or mange resources for Threat Intelligence
4.2. Workflow for Existing Scores¶
In this example, show how to edit a Score.
Navigate to
Double click on the score you would like to change. In this example double click on “Policy - Off-hours Compliance Activity to a Local Host”
Click on tab.
At the bottom double click on ‘time_hourminute’ rule. This will bring up the rule editor.
Change the time to match your companies off hour policy.
Click button to save the rule.
Change any other rules to match your companies off hour policy.
Click button to save the Score.
4.3. Workflow for New Scores¶
This example will show how to create a new score to detect possible DNS tunnel.
Navigate to
Click on button.
Give the Score a descriptive name.
Check Enabled if you would like the score to be active.
Check Public if you would like the score to be available to Child groups.
Select an Action if the rules specified match. Options are ‘Add’ or ‘Subtract’.
Enter the value you would like to Add or Subtract from the weight if the rule matches.
Select the Parent group for the Score.
Click on the tab.
In this example we want to detect Possible DNS tunnel.
Note
First object container has to be an ‘And’ container.
This Score will be using a ‘Or’ statement so the first item to add is an ‘Or’ container. Click on .
Next, add a ‘And’ container. Click on .
For the first rule, Click on .
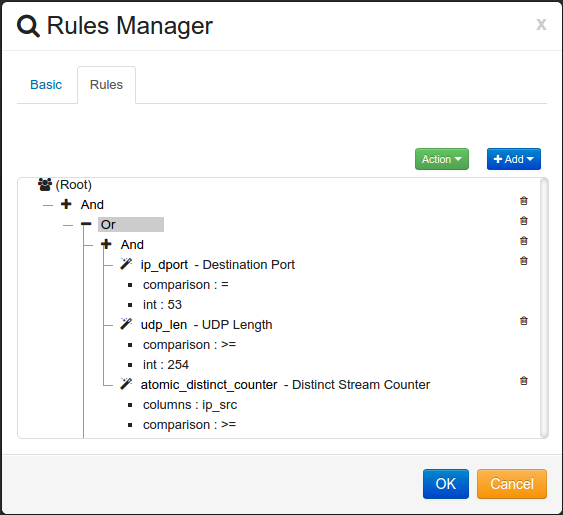
Select Destination Port (ip_dport) for the module key.
Set the Comparison to equal sign ‘=’.
Set the Value to DNS port number ‘53’.
Click button to save the rule.
Next rule, Click on .
Select UDP Length (udp_len) for the module key.
Set the Comparison to Greater Than or Equal to sign ‘>=’.
Set the Value to ‘254’.
Note
This value is setting the amount of bytes for the UDP length. Average length of valid DNS packets are between 100 - 200 bytes. DNS tunnel traffic typical uses the max allowed bytes for a DNS UDP packet which is 512 bytes. Setting it to 254 bytes helps prevent false positives.
Click button to save the rule.
Next rule, Click on .
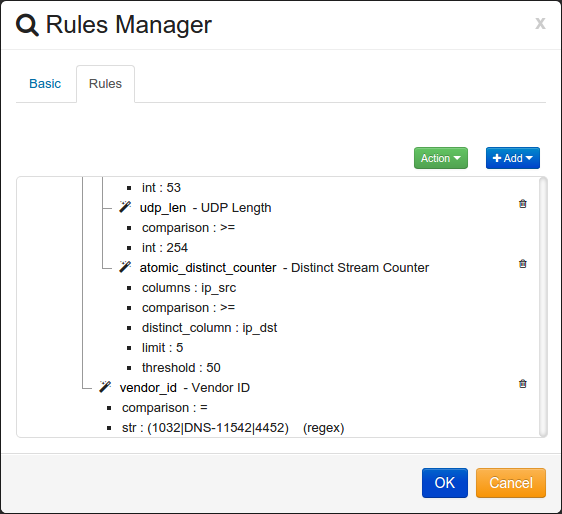
Select Distinct Stream counter (atomic_distinct_counter) Function.
Enter ‘ip_src’ in the Columns box.
Select ‘ip_dst’ for the Distinct Column. This will require all the events to have a unique Destination IP address.
Set the Comparison to Greater Than or Equal to sign ‘>=’.
Set the Threshold value to 50.
Set the Time Limit to ‘Within 5 Minutes’.
Note
Because DNS tunnels are limited to 512 Bytes per packet it requires a lot of packets in a short period of time. This rule is stating that in a 5 Minute window if the system sees 50 events from any Source IP address going to a unique Destination IP address this rule will equal True.
Click button to save the rule.
At this point the rules should look like the following:
If you have an IDS that also detects DNS tunnels you can add additional rules to look for this information.
Click on .
Select Vendor ID (vendor_id) for the Module Key.
Set the Comparison to Equal sign ‘=’.
Enter the Vendor ID in the value box. In this example we are entering in multiply Vendor ID’s using Regex: ‘(1032|DNS-11542|4452)’
Check the Regex box.
Click button to save this rule.
Note
You may have to grab this rule and move it so its included in the ‘Or’ container.
The rule should look like the following:
In order for this Score to be triggered all the rules in the ‘And’ container match or if the rule in the ‘Or’ container matches.
It processes the rules from Top to Bottom. First the Destination Port must equal 53. If the Destination Port doesn’t equal 53 the rest of the rules in the ‘And’ container are not processed. Next the UDP Length must be greater than or equal to 254 bytes. Finally, there must be 50 events in a 5 minute window from any Source IP address going to a unique Destination IP address.